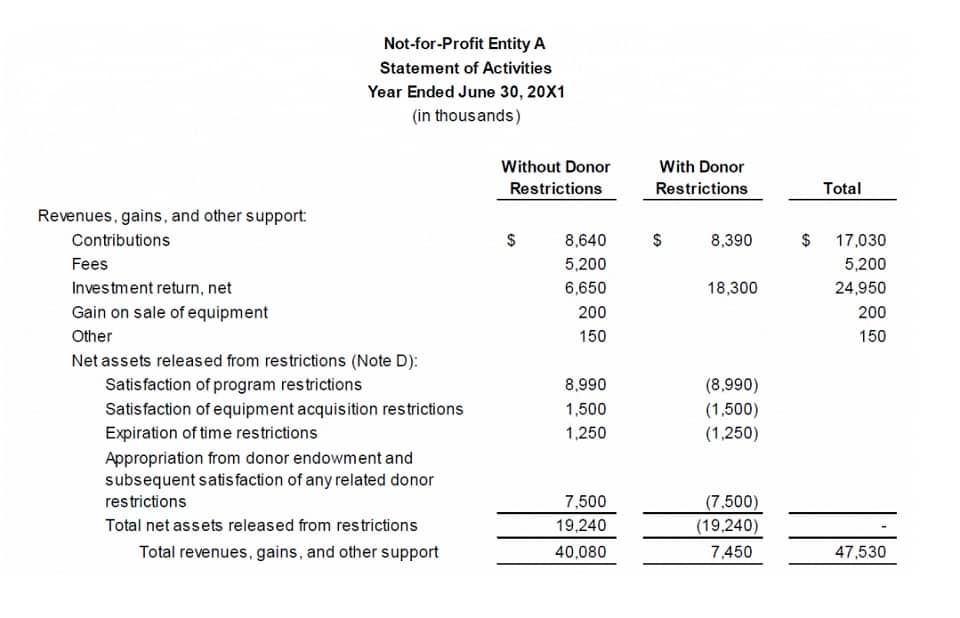
In the accounting world, goodwill arises when one company acquires another company for a higher purchase price than the fair market value of the company’s net assets. Goodwill doesn’t include any identifiable assets you can separate from the company to sell, rent, or exchange. The Foreign Currency Translation intangible assets must be acquired through purchase, not created individually. If the purchase price exceeds this net fair value, the difference is recorded as positive goodwill. A rare outcome, known as a bargain purchase, occurs if the purchase price is less than the net fair value of the acquired assets and liabilities. In a bargain purchase, the acquirer recognizes a gain on the income statement rather than recognizing goodwill.
- Unlike inherent goodwill, purchased goodwill is recorded as an intangible asset on the balance sheet and must undergo annual impairment testing to ensure its value remains accurate.
- When a company acquires another business, the purchase price often exceeds the fair value of the identifiable net assets.
- Otherwise, the goodwill stays on the balance sheet at the value assigned at the time of the transaction.
- Additionally, FASB has simplified how private companies can recognise goodwill.
Conducting goodwill impairment tests

In simple terms, goodwill is the extra value of a business that isn’t tied to a physical item. It’s things like a strong brand name, loyal customers, or a great reputation that make a business worth more than the sum of its parts. Goodwill plays a crucial role in financial reporting, impacting both the balance sheet and the profit and loss statement. Understanding goodwill accounting definition how goodwill is presented can provide deeper insights into a company’s financial health. When a subsidiary is sold, any goodwill that was originally allocated to that subsidiary is included in the calculation of the gain or loss on the sale. The amount of goodwill is determined based on the relative fair value of the subsidiary compared to the entire reporting unit.
How does goodwill work for private companies?

For such investments, one may need to estimate future cash flows using techniques like discounted cash flow (DCF) to determine their value. Accounting for business goodwill in your books requires that you subtract the fair market value of tangible assets from the total worth of the business. Goodwill is, therefore, equal to the cost of acquisition minus the value of net assets. Goodwill can positively impact a company’s financial performance by providing a competitive advantage through brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Understanding Is 401k Account Securities Account Options

Identifiable net assets are the assets and liabilities of the acquired business that can be individually identified and measured at fair value. These typically include items like cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, plant, equipment, and any liabilities. Goodwill is a reflection of the reputation, customer loyalty, and other intangible benefits that a company possesses, making it an essential consideration during mergers and acquisitions. The difference between the purchase price and the fair value of the net assets is recorded http://institutoifce.com/web/bookkeeping/understanding-debt-ratio-definition-formula/ as goodwill. Occasionally, in the FR exam, this will have been recorded incorrectly, perhaps included in the statement of financial position as part of the cost of investments and you need to make a correcting adjustment.
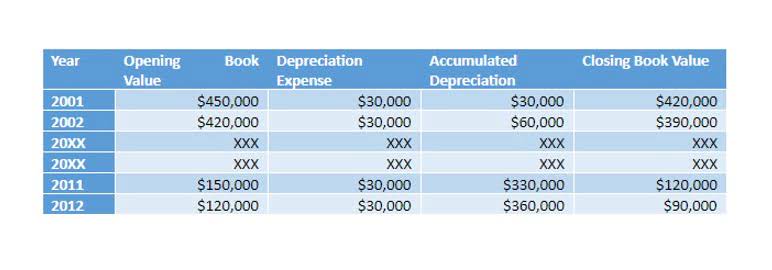
This $50 million figure is the exact amount recorded as the non-current intangible asset on Company A’s consolidated balance sheet. The second component requires the acquiring firm to meticulously assess the fair market value of every tangible and separately identifiable intangible asset and liability. Identifiable assets include physical assets like property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), as well as specific intangibles like patents and customer lists. Unlike goodwill, these specific intangible assets are typically amortized over their estimated useful lives.
Net assets at acquisition
- This method did not distinguish between who is buying whom, making it seem like the two companies were just merging rather than one acquiring the other.
- This reduction signals to the market that the acquisition is not performing as anticipated.
- Goodwill impairment can have a significant impact on a company’s financial health.
- For example, a technology company with exceptional software engineers and developers will have higher goodwill.
- If the acquired business underperforms, the company may need to write down goodwill, affecting earnings.
- While it’s possible to estimate goodwill, there’s no need to until the completion of the sale.
All you have to do is total the business assets offered by the purchased company and subtract any liabilities that the purchaser is taking on. If the acquiring company pays more than this sum, there would need to be a ‘goodwill’ accounting transaction. A crucial asset when determining a company’s overall valuation, goodwill reflects the portion of a company’s value that owners can’t ascribe to cash or physical assets. In this sense, a business’s true worth is often far more than the value of its individual, tangible, parts. In accounting, goodwill is the value of the business that exceeds its assets minus the liabilities.